Effects of climate change
EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE

What is a Climate Change ?
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its impacts on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.
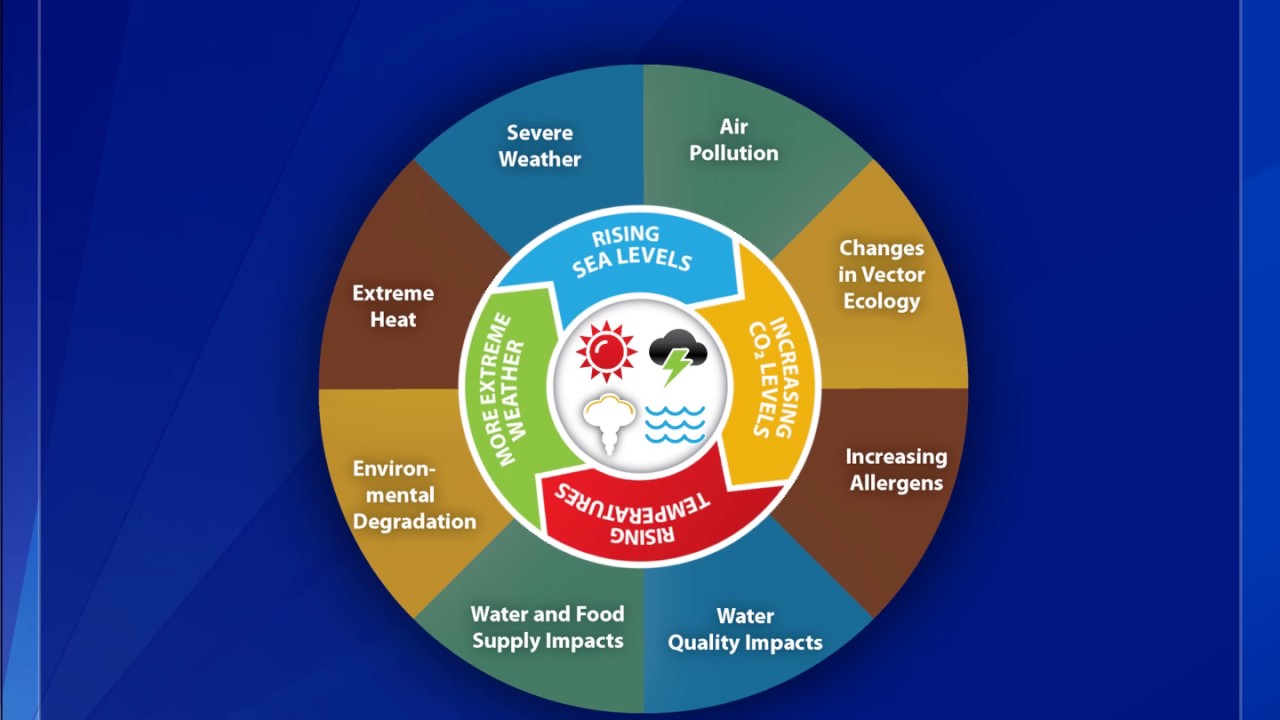
Causes and Effects of Climate Change

Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor
to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global
greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide
emissions.
As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun’s
heat. This leads to global warming and climate change. The world is now
warming faster than at any point in recorded history. Warmer
temperatures over time are changing weather patterns and disrupting the
usual balance of nature. This poses many risks to human beings and all
other forms of life on Earth.
Hotter temperatures
As greenhouse gas concentrations rise, so does the global
surface temperature. The last decade, 2011-2020, is the warmest on
record. Since the 1980s, each decade has been warmer than the previous
one. Nearly all land areas are seeing more hot days and heat waves.
Higher temperatures increase heat-related illnesses and make working
outdoors more difficult. Wildfires start more easily and spread more
rapidly when conditions are hotter. Temperatures in the Arctic have
warmed at least twice as fast as the global average.
More severe storms
Destructive storms have become more intense and more frequent
in many regions. As temperatures rise, more moisture evaporates, which
exacerbates extreme rainfall and flooding, causing more destructive
storms. The frequency and extent of tropical storms is also affected by
the warming ocean. Cyclones, hurricanes, and typhoons feed on warm
waters at the ocean surface. Such storms often destroy homes and
communities, causing deaths and huge economic losses.
Increased drought
Climate change is changing water availability, making it
scarcer in more regions. Global warming exacerbates water shortages in
already water-stressed regions and is leading to an increased risk of
agricultural droughts affecting crops, and ecological droughts
increasing the vulnerability of ecosystems. Droughts can also stir
destructive sand and dust storms that can move billions of tons of sand
across continents. Deserts are expanding, reducing land for growing
food. Many people now face the threat of not having enough water on a
regular basis.
A warming, rising ocean
The ocean soaks up most of the heat from global warming. The
rate at which the ocean is warming strongly increased over the past two
decades, across all depths of the ocean. As the ocean warms, its volume
increases since water expands as it gets warmer. Melting ice sheets also
cause sea levels to rise, threatening coastal and island communities.
In addition, the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide, keeping it from the
atmosphere. But more carbon dioxide makes the ocean more acidic, which
endangers marine life and coral reefs.
Loss of species
Climate change poses risks to the survival of species on land
and in the ocean. These risks increase as temperatures climb.
Exacerbated by climate change, the world is losing species at a rate
1,000 times greater than at any other time in recorded human history.
One million species are at risk of becoming extinct within the next few
decades. Forest fires, extreme weather, and invasive pests and diseases
are among many threats related to climate change. Some species will be
able to relocate and survive, but others will not.
Not enough food
Changes in the climate and increases in extreme weather events
are among the reasons behind a global rise in hunger and poor nutrition.
Fisheries, crops, and livestock may be destroyed or become less
productive. With the ocean becoming more acidic, marine resources that
feed billions of people are at risk. Changes in snow and ice cover in
many Arctic regions have disrupted food supplies from herding, hunting,
and fishing. Heat stress can diminish water and grasslands for grazing,
causing declining crop yields and affecting livestock.
More health risks
Climate change is the single biggest health threat facing
humanity. Climate impacts are already harming health, through air
pollution, disease, extreme weather events, forced displacement,
pressures on mental health, and increased hunger and poor nutrition in
places where people cannot grow or find sufficient food. Every year,
environmental factors take the lives of around 13 million people.
Changing weather patterns are expanding diseases, and extreme weather
events increase deaths and make it difficult for health care systems to
keep up.
Poverty and displacement
Climate change increases the factors that put and keep people
in poverty. Floods may sweep away urban slums, destroying homes and
livelihoods. Heat can make it difficult to work in outdoor jobs. Water
scarcity may affect crops. Over the past decade (2010–2019),
weather-related events displaced an estimated 23.1 million people on
average each year, leaving many more vulnerable to poverty. Most
refugees come from countries that are most vulnerable and least ready to
adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Generating power
Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels causes a
large chunk of global emissions. Most electricity is still generated by
burning coal, oil, or gas, which produces carbon dioxide and nitrous
oxide – powerful greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the
sun’s heat. Globally, a bit more than a quarter of electricity comes
from wind, solar and other renewable sources which, as opposed to fossil
fuels, emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air.
Manufacturing goods
Manufacturing and industry produce emissions, mostly from
burning fossil fuels to produce energy for making things like cement,
iron, steel, electronics, plastics, clothes, and other goods. Mining and
other industrial processes also release gases, as does the construction
industry. Machines used in the manufacturing process often run on coal,
oil, or gas; and some materials, like plastics, are made from chemicals
sourced from fossil fuels. The manufacturing industry is one of the
largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Cutting down forests
Cutting down forests to create farms or pastures, or for other
reasons, causes emissions, since trees, when they are cut, release the
carbon they have been storing. Each year approximately 12 million
hectares of forest are destroyed. Since forests absorb carbon dioxide,
destroying them also limits nature’s ability to keep emissions out of
the atmosphere. Deforestation, together with agriculture and other land
use changes, is responsible for roughly a quarter of global greenhouse
gas emissions.
Using transportation
Most cars, trucks, ships, and planes run on fossil fuels. That
makes transportation a major contributor of greenhouse gases, especially
carbon-dioxide emissions. Road vehicles account for the largest part,
due to the combustion of petroleum-based products, like gasoline, in
internal combustion engines. But emissions from ships and planes
continue to grow. Transport accounts for nearly one quarter of global
energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions. And trends point to a
significant increase in energy use for transport over the coming years.
Producing food
Producing food causes emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and
other greenhouse gases in various ways, including through deforestation
and clearing of land for agriculture and grazing, digestion by cows and
sheep, the production and use of fertilizers and manure for growing
crops, and the use of energy to run farm equipment or fishing boats,
usually with fossil fuels. All this makes food production a major
contributor to climate change. And greenhouse gas emissions also come
from packaging and distributing food.
Powering buildings
Globally, residential and commercial buildings consume over
half of all electricity. As they continue to draw on coal, oil, and
natural gas for heating and cooling, they emit significant quantities of
greenhouse gas emissions. Growing energy demand for heating and
cooling, with rising air-conditioner ownership, as well as increased
electricity consumption for lighting, appliances, and connected devices,
has contributed to a rise in energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions
from buildings in recent years.
Consuming too much
Your home and use of power, how you move around, what you eat
and how much you throw away all contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
So does the consumption of goods such as clothing, electronics, and
plastics. A large chunk of global greenhouse gas emissions are linked to
private households. Our lifestyles have a profound impact on our
planet. The wealthiest bear the greatest responsibility: the richest 1
per cent of the global population combined account for more greenhouse
gas emissions than the poorest 50 per cent.
-Garima Joshi
What is a Climate Change ?
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its impacts on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.
Causes and Effects of Climate Change

Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor
to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global
greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide
emissions.
As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun’s
heat. This leads to global warming and climate change. The world is now
warming faster than at any point in recorded history. Warmer
temperatures over time are changing weather patterns and disrupting the
usual balance of nature. This poses many risks to human beings and all
other forms of life on Earth.
Hotter temperatures
As greenhouse gas concentrations rise, so does the global
surface temperature. The last decade, 2011-2020, is the warmest on
record. Since the 1980s, each decade has been warmer than the previous
one. Nearly all land areas are seeing more hot days and heat waves.
Higher temperatures increase heat-related illnesses and make working
outdoors more difficult. Wildfires start more easily and spread more
rapidly when conditions are hotter. Temperatures in the Arctic have
warmed at least twice as fast as the global average.
More severe storms
Destructive storms have become more intense and more frequent
in many regions. As temperatures rise, more moisture evaporates, which
exacerbates extreme rainfall and flooding, causing more destructive
storms. The frequency and extent of tropical storms is also affected by
the warming ocean. Cyclones, hurricanes, and typhoons feed on warm
waters at the ocean surface. Such storms often destroy homes and
communities, causing deaths and huge economic losses.
Increased drought
Climate change is changing water availability, making it
scarcer in more regions. Global warming exacerbates water shortages in
already water-stressed regions and is leading to an increased risk of
agricultural droughts affecting crops, and ecological droughts
increasing the vulnerability of ecosystems. Droughts can also stir
destructive sand and dust storms that can move billions of tons of sand
across continents. Deserts are expanding, reducing land for growing
food. Many people now face the threat of not having enough water on a
regular basis.
A warming, rising ocean
The ocean soaks up most of the heat from global warming. The
rate at which the ocean is warming strongly increased over the past two
decades, across all depths of the ocean. As the ocean warms, its volume
increases since water expands as it gets warmer. Melting ice sheets also
cause sea levels to rise, threatening coastal and island communities.
In addition, the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide, keeping it from the
atmosphere. But more carbon dioxide makes the ocean more acidic, which
endangers marine life and coral reefs.
Loss of species
Climate change poses risks to the survival of species on land
and in the ocean. These risks increase as temperatures climb.
Exacerbated by climate change, the world is losing species at a rate
1,000 times greater than at any other time in recorded human history.
One million species are at risk of becoming extinct within the next few
decades. Forest fires, extreme weather, and invasive pests and diseases
are among many threats related to climate change. Some species will be
able to relocate and survive, but others will not.
Not enough food
Changes in the climate and increases in extreme weather events
are among the reasons behind a global rise in hunger and poor nutrition.
Fisheries, crops, and livestock may be destroyed or become less
productive. With the ocean becoming more acidic, marine resources that
feed billions of people are at risk. Changes in snow and ice cover in
many Arctic regions have disrupted food supplies from herding, hunting,
and fishing. Heat stress can diminish water and grasslands for grazing,
causing declining crop yields and affecting livestock.
More health risks
Climate change is the single biggest health threat facing
humanity. Climate impacts are already harming health, through air
pollution, disease, extreme weather events, forced displacement,
pressures on mental health, and increased hunger and poor nutrition in
places where people cannot grow or find sufficient food. Every year,
environmental factors take the lives of around 13 million people.
Changing weather patterns are expanding diseases, and extreme weather
events increase deaths and make it difficult for health care systems to
keep up.
Poverty and displacement
Climate change increases the factors that put and keep people
in poverty. Floods may sweep away urban slums, destroying homes and
livelihoods. Heat can make it difficult to work in outdoor jobs. Water
scarcity may affect crops. Over the past decade (2010–2019),
weather-related events displaced an estimated 23.1 million people on
average each year, leaving many more vulnerable to poverty. Most
refugees come from countries that are most vulnerable and least ready to
adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Generating power
Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels causes a
large chunk of global emissions. Most electricity is still generated by
burning coal, oil, or gas, which produces carbon dioxide and nitrous
oxide – powerful greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the
sun’s heat. Globally, a bit more than a quarter of electricity comes
from wind, solar and other renewable sources which, as opposed to fossil
fuels, emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air.
Manufacturing goods
Manufacturing and industry produce emissions, mostly from
burning fossil fuels to produce energy for making things like cement,
iron, steel, electronics, plastics, clothes, and other goods. Mining and
other industrial processes also release gases, as does the construction
industry. Machines used in the manufacturing process often run on coal,
oil, or gas; and some materials, like plastics, are made from chemicals
sourced from fossil fuels. The manufacturing industry is one of the
largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Cutting down forests
Cutting down forests to create farms or pastures, or for other
reasons, causes emissions, since trees, when they are cut, release the
carbon they have been storing. Each year approximately 12 million
hectares of forest are destroyed. Since forests absorb carbon dioxide,
destroying them also limits nature’s ability to keep emissions out of
the atmosphere. Deforestation, together with agriculture and other land
use changes, is responsible for roughly a quarter of global greenhouse
gas emissions.
Using transportation
Most cars, trucks, ships, and planes run on fossil fuels. That
makes transportation a major contributor of greenhouse gases, especially
carbon-dioxide emissions. Road vehicles account for the largest part,
due to the combustion of petroleum-based products, like gasoline, in
internal combustion engines. But emissions from ships and planes
continue to grow. Transport accounts for nearly one quarter of global
energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions. And trends point to a
significant increase in energy use for transport over the coming years.
Producing food
Producing food causes emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and
other greenhouse gases in various ways, including through deforestation
and clearing of land for agriculture and grazing, digestion by cows and
sheep, the production and use of fertilizers and manure for growing
crops, and the use of energy to run farm equipment or fishing boats,
usually with fossil fuels. All this makes food production a major
contributor to climate change. And greenhouse gas emissions also come
from packaging and distributing food.
Powering buildings
Globally, residential and commercial buildings consume over
half of all electricity. As they continue to draw on coal, oil, and
natural gas for heating and cooling, they emit significant quantities of
greenhouse gas emissions. Growing energy demand for heating and
cooling, with rising air-conditioner ownership, as well as increased
electricity consumption for lighting, appliances, and connected devices,
has contributed to a rise in energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions
from buildings in recent years.
Consuming too much
Your home and use of power, how you move around, what you eat
and how much you throw away all contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
So does the consumption of goods such as clothing, electronics, and
plastics. A large chunk of global greenhouse gas emissions are linked to
private households. Our lifestyles have a profound impact on our
planet. The wealthiest bear the greatest responsibility: the richest 1
per cent of the global population combined account for more greenhouse
gas emissions than the poorest 50 per cent.
-Garima Joshi
What is a Climate Change ?
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its impacts on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.
Causes and Effects of Climate Change
Fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – are by far the largest contributor to global climate change, accounting for over 75 per cent of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 per cent of all carbon dioxide emissions.
As greenhouse gas emissions blanket the Earth, they trap the sun’s heat. This leads to global warming and climate change. The world is now warming faster than at any point in recorded history. Warmer temperatures over time are changing weather patterns and disrupting the usual balance of nature. This poses many risks to human beings and all other forms of life on Earth.
Hotter temperatures
As greenhouse gas concentrations rise, so does the global surface temperature. The last decade, 2011-2020, is the warmest on record. Since the 1980s, each decade has been warmer than the previous one. Nearly all land areas are seeing more hot days and heat waves. Higher temperatures increase heat-related illnesses and make working outdoors more difficult. Wildfires start more easily and spread more rapidly when conditions are hotter. Temperatures in the Arctic have warmed at least twice as fast as the global average.
More severe storms
Destructive storms have become more intense and more frequent in many regions. As temperatures rise, more moisture evaporates, which exacerbates extreme rainfall and flooding, causing more destructive storms. The frequency and extent of tropical storms is also affected by the warming ocean. Cyclones, hurricanes, and typhoons feed on warm waters at the ocean surface. Such storms often destroy homes and communities, causing deaths and huge economic losses.
Increased drought
Climate change is changing water availability, making it scarcer in more regions. Global warming exacerbates water shortages in already water-stressed regions and is leading to an increased risk of agricultural droughts affecting crops, and ecological droughts increasing the vulnerability of ecosystems. Droughts can also stir destructive sand and dust storms that can move billions of tons of sand across continents. Deserts are expanding, reducing land for growing food. Many people now face the threat of not having enough water on a regular basis.
A warming, rising ocean
The ocean soaks up most of the heat from global warming. The rate at which the ocean is warming strongly increased over the past two decades, across all depths of the ocean. As the ocean warms, its volume increases since water expands as it gets warmer. Melting ice sheets also cause sea levels to rise, threatening coastal and island communities. In addition, the ocean absorbs carbon dioxide, keeping it from the atmosphere. But more carbon dioxide makes the ocean more acidic, which endangers marine life and coral reefs.
Loss of species
Climate change poses risks to the survival of species on land and in the ocean. These risks increase as temperatures climb. Exacerbated by climate change, the world is losing species at a rate 1,000 times greater than at any other time in recorded human history. One million species are at risk of becoming extinct within the next few decades. Forest fires, extreme weather, and invasive pests and diseases are among many threats related to climate change. Some species will be able to relocate and survive, but others will not.
Not enough food
Changes in the climate and increases in extreme weather events are among the reasons behind a global rise in hunger and poor nutrition. Fisheries, crops, and livestock may be destroyed or become less productive. With the ocean becoming more acidic, marine resources that feed billions of people are at risk. Changes in snow and ice cover in many Arctic regions have disrupted food supplies from herding, hunting, and fishing. Heat stress can diminish water and grasslands for grazing, causing declining crop yields and affecting livestock.
More health risks
Climate change is the single biggest health threat facing humanity. Climate impacts are already harming health, through air pollution, disease, extreme weather events, forced displacement, pressures on mental health, and increased hunger and poor nutrition in places where people cannot grow or find sufficient food. Every year, environmental factors take the lives of around 13 million people. Changing weather patterns are expanding diseases, and extreme weather events increase deaths and make it difficult for health care systems to keep up.
Poverty and displacement
Climate change increases the factors that put and keep people in poverty. Floods may sweep away urban slums, destroying homes and livelihoods. Heat can make it difficult to work in outdoor jobs. Water scarcity may affect crops. Over the past decade (2010–2019), weather-related events displaced an estimated 23.1 million people on average each year, leaving many more vulnerable to poverty. Most refugees come from countries that are most vulnerable and least ready to adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Generating power
Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels causes a large chunk of global emissions. Most electricity is still generated by burning coal, oil, or gas, which produces carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide – powerful greenhouse gases that blanket the Earth and trap the sun’s heat. Globally, a bit more than a quarter of electricity comes from wind, solar and other renewable sources which, as opposed to fossil fuels, emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air.
Manufacturing goods
Manufacturing and industry produce emissions, mostly from burning fossil fuels to produce energy for making things like cement, iron, steel, electronics, plastics, clothes, and other goods. Mining and other industrial processes also release gases, as does the construction industry. Machines used in the manufacturing process often run on coal, oil, or gas; and some materials, like plastics, are made from chemicals sourced from fossil fuels. The manufacturing industry is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
Cutting down forests
Cutting down forests to create farms or pastures, or for other reasons, causes emissions, since trees, when they are cut, release the carbon they have been storing. Each year approximately 12 million hectares of forest are destroyed. Since forests absorb carbon dioxide, destroying them also limits nature’s ability to keep emissions out of the atmosphere. Deforestation, together with agriculture and other land use changes, is responsible for roughly a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Using transportation
Most cars, trucks, ships, and planes run on fossil fuels. That makes transportation a major contributor of greenhouse gases, especially carbon-dioxide emissions. Road vehicles account for the largest part, due to the combustion of petroleum-based products, like gasoline, in internal combustion engines. But emissions from ships and planes continue to grow. Transport accounts for nearly one quarter of global energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions. And trends point to a significant increase in energy use for transport over the coming years.
Producing food
Producing food causes emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases in various ways, including through deforestation and clearing of land for agriculture and grazing, digestion by cows and sheep, the production and use of fertilizers and manure for growing crops, and the use of energy to run farm equipment or fishing boats, usually with fossil fuels. All this makes food production a major contributor to climate change. And greenhouse gas emissions also come from packaging and distributing food.
Powering buildings
Globally, residential and commercial buildings consume over half of all electricity. As they continue to draw on coal, oil, and natural gas for heating and cooling, they emit significant quantities of greenhouse gas emissions. Growing energy demand for heating and cooling, with rising air-conditioner ownership, as well as increased electricity consumption for lighting, appliances, and connected devices, has contributed to a rise in energy-related carbon-dioxide emissions from buildings in recent years.
Consuming too much
Your home and use of power, how you move around, what you eat and how much you throw away all contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. So does the consumption of goods such as clothing, electronics, and plastics. A large chunk of global greenhouse gas emissions are linked to private households. Our lifestyles have a profound impact on our planet. The wealthiest bear the greatest responsibility: the richest 1 per cent of the global population combined account for more greenhouse gas emissions than the poorest 50 per cent.
-Garima Joshi
Comments
Post a Comment